Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
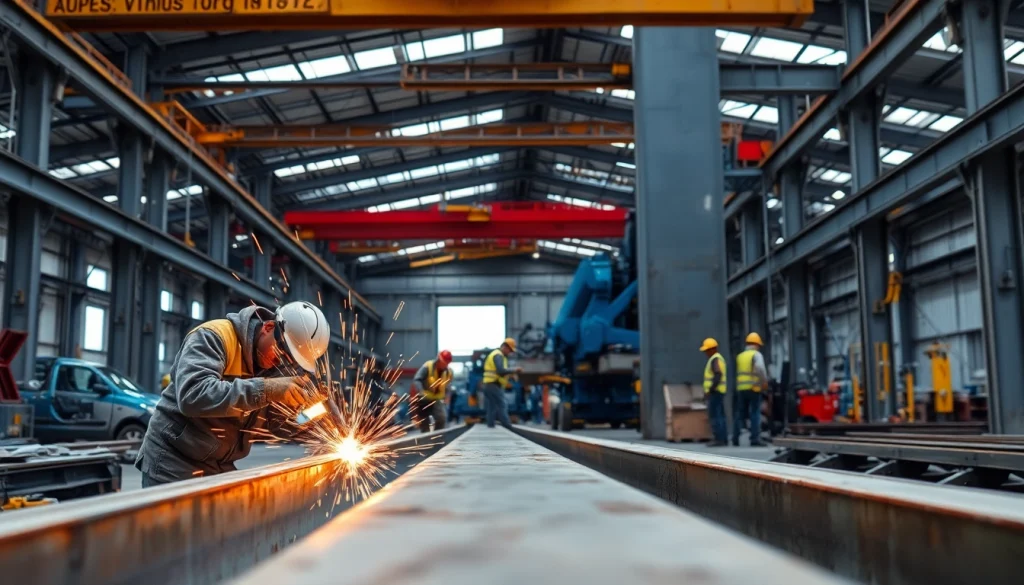
Structural steel fabrication is a crucial process that plays a significant role in the construction industry. It involves the cutting, shaping, and assembling of steel structures that serve as the backbone of various buildings and infrastructure. From skyscrapers to bridges, the efficacy of these fabricated steel components often determines the safety and durability of the entire structure. This article delves deep into the intricacies of structural steel fabrication, its applications, techniques, and future trends, providing a comprehensive guide for industry professionals and enthusiasts alike.
What is Structural Steel Fabrication?
Structural steel fabrication is the process of transforming raw steel into various structural components used in construction. This transformation typically involves several processes, including cutting, welding, bending, and assembling steel parts. Fabrication can be done in a factory or at a job site, resulting in pre-manufactured elements that can be delivered to the construction site for installation.
The complexities of this process require specialized knowledge and equipment. It includes both standard practices and innovative methods tailored to meet specific project requirements. Critical to the industry, structural steel fabrication ensures that the materials used meet the specifications for load-bearing strength, flexibility, and resilience against environmental stresses.
The Importance of Quality Materials
Quality materials are paramount in structural steel fabrication. The selection of steel grade affects the performance and longevity of the finished product. High-grade steel, such as ASTM A992 and A36, is often used for their superior mechanical properties and reliability. Furthermore, advancements in metallurgical engineering have introduced new alloys and composite materials that enhance the strength-to-weight ratio, providing more options to meet project specifications.
Additionally, ensuring that all materials used comply with industry standards is non-negotiable. Regular inspections and certifications from reputable sources can help mitigate risks associated with inferior materials, such as structural failures, and also ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Common Applications in Construction
Structural steel is utilized across a broad spectrum of applications in construction. Some of the most common uses include:
- Buildings: From commercial skyscrapers to residential homes, structural steel forms frames and supports that endure significant loads.
- Bridges: Steel’s strength and durability make it a preferred material for constructing bridges, enabling them to span large distances while supporting vehicular and pedestrian traffic.
- Industrial Facilities: Many manufacturing plants and warehouses are built with steel frameworks, allowing for large open spaces and efficient material handling.
- Monuments and Towers: Iconic structures such as radio towers and observation decks often utilize steel for its lightweight and strong characteristics.
Key Techniques in Structural Steel Fabrication
The fabrication of structural steel involves a variety of techniques and methods, each playing a vital role in the final product’s quality and performance. Understanding these techniques can help industry professionals choose the right method for their specific needs and ensure high standards of safety and efficiency.
Welding Methods and Technologies
Welding is one of the core processes in structural steel fabrication. Various welding techniques are employed to join steel pieces securely. Some of the commonly used methods include:
- MIG Welding: Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding is a versatile and efficient technique that uses a continuous wire feed and an inert gas to protect the weld pool from contamination.
- TIG Welding: Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding allows for precise control over the weld and is often used for more delicate work or thinner sections of steel.
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding: This method uses a tubular wire filled with flux to create a shielding gas during the welding process, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
Specialized equipment and skilled technicians are essential for ensuring high-quality welds that can withstand the stresses encountered in construction.
CNC Machining in Steel Fabrication
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized structural steel fabrication. This technology enables precise cuts and shapes that traditional machining methods may not achieve. CNC machines can drill holes, cut sections, and create complex geometries with minimal waste and high repeatability.
Utilizing CNC technology not only increases efficiency but also reduces human error, guaranteeing that each component meets the required specifications. These machines can work with several types of steel and other materials, allowing for greater flexibility in project design and execution.
Finishing Processes to Enhance Durability
Once steel components are fabricated, additional finishing processes may be necessary to enhance their durability and aesthetic appeal. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings, such as galvanization or powder coating, can prevent rust and corrosion, prolonging the life of the structure.
- Sanding and Polishing: These techniques improve surface finish and remove imperfections, contributing to the overall appearance and functionality of the steel.
- Heat Treatment: This process can modify the microstructure of the steel to improve hardness, strength, or ductility, making it better suited for specific applications.
Investing time and resources in these finishing processes can lead to significant long-term savings by preventing premature deterioration and maintaining structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Fabrication Partner
Selecting the right fabrication partner is a pivotal decision that can directly influence the success of a construction project. The complexity of fabrication requires collaboration with a partner who has the necessary experience, expertise, and technological capabilities.
Evaluating Experience and Expertise
When choosing a fabrication partner, consider their industry experience and expertise. A company with a proven track record in structural steel fabrication will understand the nuances of different projects and provide reliable solutions. Specifically, look for:
- Years in Operation: Longer tenure typically correlates with broader experience and deeper industry knowledge.
- Project Portfolio: Review past projects to gauge the quality and complexity of their work.
- Certifications: Industry-standard certifications (e.g., ISO, AWS) can indicate compliance with quality and safety regulations.
Assessing Technological Capabilities
In a rapidly evolving industry, the technological capabilities of a fabrication partner can significantly affect the outcome of a project. Evaluate their use of modern technologies, such as:
- CNC machinery for precision fabrication.
- Robotic welding for efficiency and consistency.
- Advanced software for design and project management.
A partner that embraces new technologies will likely offer innovative solutions that can reduce costs and improve timelines.
Client Testimonials and Case Studies
Looking at client testimonials and case studies can provide insights into a fabrication partner’s reliability and effectiveness. Positive reviews can serve as indicators of a company’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, detailed case studies can demonstrate their approach to problem-solving and project management.
Reaching out to previous clients to discuss their experiences can also yield valuable information about how the partner handles challenges and adapts to changing project needs.
Challenges in Structural Steel Fabrication
Despite its many advantages, structural steel fabrication also presents unique challenges that industry stakeholders must navigate. Understanding these challenges is fundamental to implementing effective solutions and ensuring the smooth execution of projects.
Addressing Material Waste and Efficiency
One of the most significant challenges in structural steel fabrication is managing material waste. Issues such as cutting errors, overproduction, and improper handling can lead to substantial waste, impacting both costs and the environment.
To mitigate these issues, utilizing advanced software for inventory management and material optimization can minimize waste. Implementing lean manufacturing principles can also enhance efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing excess materials.
Techniques for Reducing Lead Time
Timely project completion is essential in construction, and delays in steel fabrication can significantly impact project schedules. To reduce lead times, fabrication companies can:
- Adopt just-in-time (JIT) production strategies to ensure materials are produced and delivered precisely when needed.
- Implement real-time tracking systems to monitor progress and address delays promptly.
- Foster strong relationships with suppliers to ensure reliable access to quality materials.
By strategically managing these elements, fabrication partners can help ensure smooth project execution without sacrificing quality.
Ensuring Compliance with Safety Standards
Safety is paramount in construction, and structural steel fabrication must adhere to stringent safety standards and regulations. Companies must incorporate safety measures into every aspect of the fabrication process, including:
- Regular safety training for employees.
- Implementing standardized operating procedures.
- Conducting routine safety audits and inspections.
Ensuring compliance with safety standards not only protects workers but also reduces liability and enhances the company’s reputation in the industry.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Fabrication
The field of structural steel fabrication is continually evolving, influenced by advancements in technology and shifts in industry demands. Keeping abreast of these trends can offer a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Impact of Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are shaping the future of structural steel fabrication, providing greater efficiency and precision. Automated systems can enhance productivity by performing repetitive tasks, such as welding and assembly, with minimal human intervention. This not only reduces labor costs but also improves consistency and quality in fabricated products.
As automation technology continues to advance, it is expected that more fabrication shops will implement these systems to remain competitive and meet increasing project demands.
Emerging Materials and Sustainable Practices
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability within the construction industry, prompting a shift toward the use of emerging materials and sustainable practices in structural steel fabrication. Recyclability of steel, innovative composite materials, and eco-friendly design principles are gaining traction.
By focusing on sustainability, companies can not only reduce environmental impacts but also align with increasing regulatory requirements and client preferences for green practices.
Innovative Design Software in Fabrication
The integration of innovative design software is revolutionizing the design and fabrication process. Advanced modeling tools, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), allow for a comprehensive approach to project planning and execution. These tools enable teams to visualize the entire construction project, facilitating better collaboration, communication, and efficiency.
Furthermore, design software can assist in optimizing material usage and production schedules, leading to reduced costs and improved timelines throughout the fabrication process.